Auto parts machining technology:
1. Casting;
2. Forging;
3. Welding;
4. Cold stamping;
5. Metal cutting;
6. Heat treatment;
7. Assembly.

Forging is a manufacturing method in which molten metal material is poured into a mold cavity, cooled and solidified to obtain a product. In the automobile industry, many parts are made of pig iron in pig iron, accounting for about 10% of the net weight of the vehicle, such as cylinder liners, gearbox housings, steering system housings, automobile rear axle housings, brake system drums, various Sand molds are generally used for the production of cast iron parts such as brackets.
In the automotive industry, the production method of casting is widely used. Forging is divided into random forging and entity model forging. Random forging is a production method in which metal material blanks are placed on iron felts to withstand impact or burden, also known as “quenching”. The blanks of vehicle worm gears and shafts are produced and processed by random casting. Solid model forging is a production method in which metal blanks are placed in the cavity of a forging die to withstand impact or load. Solid model forging is somewhat like the whole process of batter being rolled into cookies in a template.
Cold die or sheet stamping die is a production method in which a sheet of metal material is cut or formed under force in a stamping die. Daily necessities, such as braised pots, lunch boxes, washbasins, etc., are all made by cold stamping. The auto parts produced and processed by cold stamping die include: auto engine oil pan, brake system bottom plate, auto window frame and most body parts. Such parts are generally formed by blanking, punching, bending, reverse edge, trimming and other processes. In order to better produce cold stamping parts, stamping dies need to be made.
Electric welding is a production method in which two metal materials are locally heated or simultaneously heated and stamped. Generally, one hand holds the mask, and the other hand holds the electric welding tongs and welding wire connected with the cable, which is called manual arc welding. However, manual arc welding is rarely used in the automotive industry, and it is most widely used in car body production. The most important thing is welding. Welding is suitable for welding cold-rolled steel sheets by electric welding. In actual operation, two electrodes are used to pressurize two thick steel plates to make them bond together, and at the same time, heat and melt the current flow at the meeting point to make a firm and tight connection.
Metal material turning production and machining is to use milling cutter to drill metal material blank step by step; so that the product can obtain the required product appearance, specification and roughness. The turning production and machining of metal materials includes two methods: milling and machining. Milling is a production method in which employees use hand-made tools for cutting. The operation is sensitive and convenient, and it is widely used for installation and maintenance. machining and manufacturing rely on CNC lathes to realize drilling, including: turning, planing, milling, drilling, grinding and other methods.
The heat treatment process is a way to reheat, insulate or cool solid steel to change its structure to meet the application or technical standards of the part. The temperature of the heating environment, the length of the holding time, and the speed of the cooling efficiency will cause different structural changes in the steel. Blacksmiths infiltrate heated cast iron into water to cool it quickly (called heat treatment), which can increase the strength of aluminum parts, which is also a case of heat treatment processes. Heat treatment methods include quenching, quenching, heat treatment, quenching, and the like.
Then according to certain regulations, the various components are connected to each other to form a complete vehicle. Whether it is a component or a complete vehicle, it needs to cooperate and relate to each other according to the requirements of the design drawings, so that the components or the complete vehicle can achieve the set characteristics. For example, when installing the transmission to the clutch housing, make sure that the axis of the transmission key shaft and the axis of the crankshaft are pointing. This core method is not adjusted by the installer (miller) during assembly, but only by the design and production adjustment.
Some common CNC machining technologies used in the automotive industry include:
1. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) Machining: CNC machines are automated tools controlled by a computer program. They can perform precise and complex machining operations, such as milling, turning, drilling, and grinding. CNC machining ensures high accuracy and repeatability, making it ideal for mass production of auto parts.
2. Milling: Milling involves the use of rotary cutters to remove material from a workpiece. It is used to create flat surfaces, slots, and complex shapes in automotive components.
3. Turning: Turning is used to produce cylindrical parts, such as shafts and axles. The workpiece rotates, and a cutting tool removes material to achieve the desired shape.
4. Drilling: Drilling is employed to create holes in automotive parts, which are often necessary for assembly or to accommodate other components.
5. Grinding: Grinding uses abrasive wheels to remove small amounts of material and achieve tight tolerances or smooth surface finishes on auto parts.
6. Boring: Boring is used to enlarge existing holes or create precise internal features in automotive components.
7. Electrochemical Machining (ECM): ECM is a non-traditional machining process that uses electrochemical reactions to remove material. It is suitable for complex shapes and heat-sensitive materials.
8. Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): EDM uses electrical sparks to erode material from the workpiece. It is often used for intricate shapes and hardened materials.
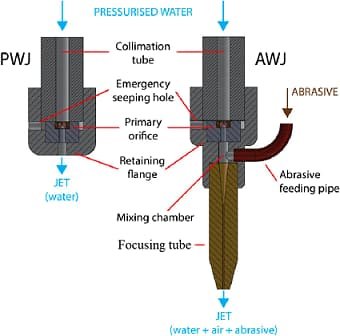
9. Waterjet Cutting: Waterjet cutting involves the use of a high-pressure jet of water (sometimes mixed with abrasive materials) to cut through various materials used in auto parts.
Automotive manufacturers choose specific machining technologies based on factors like the material properties of the auto parts, required tolerances, production volume, and cost-effectiveness.
With the advancement of technology, automation, robotics, and data-driven manufacturing systems are becoming more prevalent in the automotive industry. These technologies improve efficiency, reduce production time, and enhance quality control in auto parts machining processes.